Introduction
The substrate and protease binding model and nomenclature used in this software is popularly accepted and used and was given by Schechter and Berger [1]. The substrate comes and binds to specific binding sites present on the protease. Substrate here refers to protein present in the food source and protease refers to the protein digesting enzymes present in the human body. Schematic representation of the substrate-protease complex has been provided in the figure below [Fig-1]. For this web server the nomenclature used is as follows:The sub-sites on the protease are named "S1-S4" on the left side of the point of cleavage and “S1’-S4’” on the right side of the point of cleavage. Similarly the amino acids on the substrate were named as “P1-P4” on the N terminal end of the point of cleavage and “P1’-P4’” on the C terminal end of the point of cleavage.
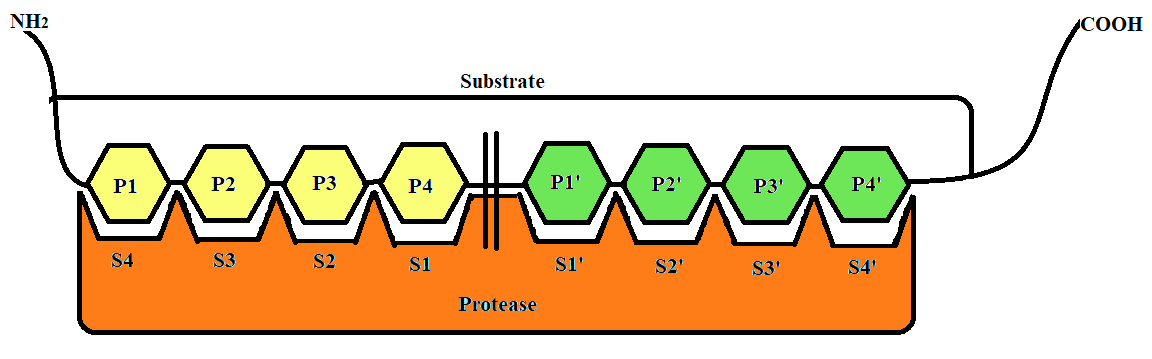
Fig 1 - Schematic representation of substrate-protease complex and its nomenclature
For simplicity only substrate part is represented in the examples given below. The protease and substrate may interact at other places but to generalize and simplify only the interaction of eight amino acids has been considered with the substrate. Detailed description of the proteases used and their specific cut site is given below.
Proteases naturally present in Human Body
-
Enzyme Name: Elastase
1
|
Gene: CELA1 Uniprot ID: Q9UNI1 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.21.36 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: na |
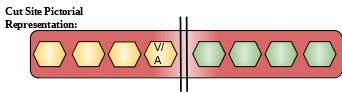
Cut Site: Hydrolysis of proteins, including elastin. Preferential cleavage: Ala-|-Xaa.
Description: They belong to the family of serine proteases. Humans have six elastase genes which encode structurally similar proteins elastase 1, 2, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B. The encoded preprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the active protease. Elastase 1 is only expressed in skin keratinocytes. They are not expressed in pancreas as are other elastases.[2]
Deficiency: Elastase 1 is known to be associated with diseases like Steatorrhea and Pancreatic Acinar Cell Adenocarcinoma.
-
Enzyme
Name: Neutrophil
elastase (Elastase 2)
|
Gene: ELANE Uniprot ID: P08246 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.21.37 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 2RG3, 5A0A, 2Z7F
|
Protein Figure:
|
Cut Site: Hydrolysis of proteins, including elastin. Preferential cleavage: Val-|-Xaa > Ala-|-Xaa.
Description: They belong to the family of serine proteases. Humans have six elastase genes which encode structurally similar proteins elastase 1, 2, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B.. The encoded preprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the active protease. The enzyme may play a role in degenerative and inflammatory diseases through proteolysis of collagen-IV and elastin. It also inhibits C5a-dependent neutrophil enzyme release and chemotaxis.[3]
Deficiency: Mutations in this gene are related with cyclic neutropenia and severe congenital neutropenia (SCN). Neutropenia is a condition in which the number of neutrophils in our body decreases.
-
Enzyme
Name: Chymotrypsinogen
B1
|
Gene: CTRB1 Uniprot ID: P17538 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.21.1 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: na |
Cut Site: Preferential cleavage: Tyr-|-Xaa, Trp-|-Xaa, Phe-|-Xaa, Leu-|-Xaa
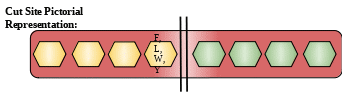
Description: Chymotrypsinogen B1 is a protein from serine protease family of protease. These proteins are secreted in the cells of pancreas and are released in small intestine. They then undergo activation in small intestine. They cleave their substrate in small intestine.[4]
Deficiency: Inactivation of chymotrypsinogen will lead to digestion related problems.
-
Enzyme
Name: Chymotrypsin-C
|
Gene: CTRC Uniprot ID: Q99895 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.21.2 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 4H4F
|
Protein Figure:
|
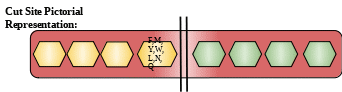
Description: Chymotrypsinogen C is a protein from serine protease family of protease. This protein acts as a serum calcium decreasing factor. They also regulates activation and degradation of trypsinogen and procarboxypeptidase.[5]
Deficiency: Chymotrypsin C is related with diseases like Pancreatitis.
-
Enzyme
Name: Pancreatic
Endopeptidase E
|
Gene: CELA3A Uniprot ID: P09093 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.21.70 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: na |
Cut Site: Preferential cleavage: Ala-|-Xaa. Does not hydrolyze elastin.
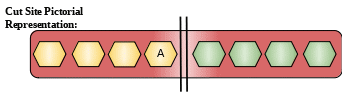
Description: They belong to the family of serine proteases. Humans have six elastase genes which encode structurally similar proteins elastase 1, 2, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B. The encoded preprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the active protease. These proteins are secreted in the cells of pancreas and are released in small intestine. They then undergo activation in small intestine. They cleave their substrate in small intestine. They also help in intestinal transport and metabolism.[6]
Deficiency: Pancreatic Endopeptidase E is related with diseases like Holoprosencephaly.
-
Enzyme
Name: Enteropeptidase
|
Gene: TMPRSS15 Uniprot ID:P98073 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.21.9 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 4DGJ
|
Protein Figure:
|
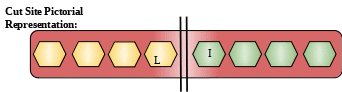
Description: These protein belongs to the family of trypsin peptidases which is a subpart of serine proteases. They consist of two chains joined together by disulfide bond. They are responsible for converting trypsinogen to trypsin.[7]
Deficiency: Mutation in this gene causes Enterokinase deficiency and Hymenolepiasis. Enterokinase deficiency is malabsorption disorders which may lead to diarrhea and other related problems. Hymenolepiasis is small intestine related diseases which is caused by infestation by tapeworm.
-
Enzyme
Name: Prostasin
-
Gene: PRSS8
Uniprot ID: Q16651
Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans)
EC Number: EC:3.4.21.-
Enzyme Category: hydrolases
PDB ID: 3DFJ, 3GYL, 3E16
Protein Figure:
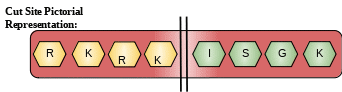
Cut Site: RKRK-ISGK Possesses a trypsin-like cleavage specificity with a preference for poly-basic substrate
Description: These proteins belong to chymotrypsin family of serine protease. Its active form consist of two chains joined together by disulfide bond. The active enzyme is expressed in prostate epithelia in huge amount. It shows trypsin like substrate specificity. Apart from that it also proteolytically activates epithelial sodium channel. [8]
Deficiency:
Prostatin
is related to diseases like Follicular Ichthyosis and Chromophobe
Renal Cell Carcinoma.
-
Enzyme
Name: Trypsin
- 1
|
Gene: PRSS1 Uniprot ID: P07477 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.21.4 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 1FXY, 2RA3, 4WWY
|
Protein Figure:
|
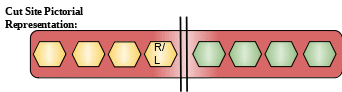
Cut Site: Preferential cleavage: Arg-|-Xaa, Lys-|-Xaa.
Description: These protein belongs to the family of trypsin peptidases which is a subpart of serine proteases. These proteins are secreted in the cells of pancreas and are released in small intestine. They then undergo activation in small intestine. These genes are present on chromosome 7.[9]
Deficiency: Mutations in this gene are associated with hereditary pancreatitis.
-
Enzyme
Name:
Pepsin
|
Gene: PGA4 Uniprot ID: P0DJD7 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.23.1 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 1PSO, 1PSN, 1QRP
|
Protein Figure:
|
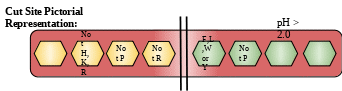
Cut Site: Due to broad specificity of pepsin there are two types of cut site are present.
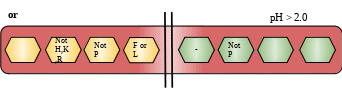
Description: This protein belongs to peptidase A1 family of endopeptidases. The encoded precursor is secreted by gastric chief cells. These proteins converts to active form in acidic conditions of the stomach. This protein helps in the digestion of dietary proteins. Deficiency: Pepsinogen levels in serum may serve as a biomarker for atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. So changes in its level may affect these diseases in one or the other form.[10]
-
Enzyme
Name: Gastricsin
|
Gene: PGC Uniprot ID: P20142 Organism: Homo sapiens (Humans) EC Number: EC:3.4.23.3 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 1AVF, 1HTR
|
Protein Figure:
|
Cut Site: More restricted specificity than pepsin A, but shows preferential cleavage at Tyr-|-Xaa bonds. High activity on hemoglobin.
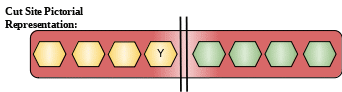
Description: This protein belongs to family of aspartic proteinase. This protein is secreted in stomach and forms an important component of gastric mucosa. This protein becomes active in acidic conditions itself. [11]
Deficiency: Mutations in this gene or inactivation of this protein are related to gastric cancers. Also its expression level in serum may serve as a biomarker for atrophic gastritis.
External Proteases
-
Enzyme
Name:
Fruit Bromelain
|
Gene: na Uniprot ID: O23791 Organism: Ananas comosus (Pineapple) (Ananas ananas) EC Number: EC:3.4.22.33 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: na |
Cut Site: Hydrolysis of proteins with broad specificity for peptide bonds. Bz-Phe-Val-Arg-|-NHMec is a good synthetic substrate[12]
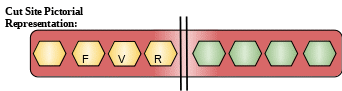
Description: It is a type of glucoprotein proteinase. It is extracted from pineapple. Fruit Bromelain has many medical as well as industrial applications. It is also used in the prevention of diarrhoea, digestive aids, antithrombotic, oedema treatment and osteoarthritis and promotes the absorption of antibiotic drugs. It also has immunological effect by regulating and activating immune cells and their cytokine production. It is also related to blood coagulation, fibrinolysis, and platelet functions.[13]
-
Enzyme
Name:
Stem Bromelain
|
Gene: na Uniprot ID: P14518 Organism: Ananas comosus (Pineapple) (Ananas ananas) EC Number: EC:3.4.22.32 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: na |
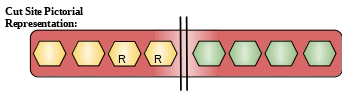
Description: It is a part of bromelain family and belongs to the class of cysteine endopeptidase. It is extracted from pineapple and forms major part of pineapple proteolytic enzyme. It has great therapeutic value. It is responsible for reversible inhibition of platelet aggregation, bronchitis, sinusitis, surgical traumas, and thrombophlebitis. It also causes enhanced absorption of drugs. It also shows anti-metastasis and anti-inflammatory activities.
-
Enzyme
Name:
Ananain
|
Gene: AN1 Uniprot ID: P80884 Organism: Ananas comosus (Pineapple) (Ananas ananas) EC Number: EC:3.4.22.31 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: na |

Description: Ananain is a part of cysteine protease and comes from stem of a pineapple. It contains around seven cysteine residues and has high structural similarity with caricain and papain. It is strongly inhibited by chicken egg-white cystatin. For full activation of the enzyme the presence of a reducing agent required. Due to its high activity, ananain can also be considered as a debriding agent for burn injuries.
-
Enzyme
Name:
Papaya proteinase 4
|
Gene: na Uniprot ID: P05994 Organism: Carica papaya (Papaya) EC Number: EC:3.4.22.25 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 1GEC
|
Protein Figure:
|
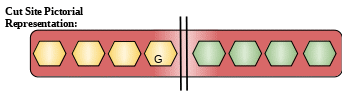
Description: It belongs to the cysteine family of proteases. But unlike other members of cysteine family protease, it does not get inhibited by chicken cystatin. This is attributed to the presence of conserved Gly residue. Similarly there are other amino acid substitution which are responsible for its unusual activity and makes it different from other family members.
-
Enzyme
Name:
Chymopapain
|
Gene: na Uniprot ID: P14080 Organism: Carica papaya (Papaya) EC Number: EC:3.4.22.6 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 1YAL
|
Protein Figure:
|
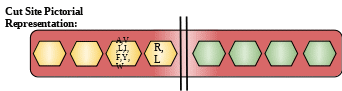
Description: It is extracted from the latex of papaya. It belongs to the family of cysteine peptidase. It has great medicinal use. Chymopapain was also taken in form of injections. It was injected directly into a herniated disk in the spine to dissolve part of the disk and relieve the pain and other problems caused by the disk pressing on a nerve. But these injections also had some side effects. So they were discontinued.
-
Enzyme
Name:
Caricain
|
Gene: na Uniprot ID: P10056 Organism: Carica papaya (Papaya) EC Number: EC:3.4.22.30 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 1MEG, 1PCI, 1PP0
|
Protein Figure:
|

Description: Caricain is obtained from papaya plant,Carica papaya. It is an example of enzyme therapy. Caricain has the ability to detoxify gliadin in whole wheat flour by proteolytically cleaving it. Thus caricain can be used in developing bread suitable for coeliacs and gluten intolerant individuals.
-
Enzyme
Name:
Chymosin
|
Gene: CYM Uniprot ID: P00794 Organism: Bos taurus (Bovine) EC Number: EC:3.4.23.4 Enzyme Category: hydrolases PDB ID: 4AUC, 3CMS, 1CZI
|
Protein Figure:
|
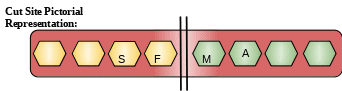
Description: Chymosin is also known as renin. Though it is mainly found in young animals, it is also found in human infants for a very short period of time. Its main function is to coagulate milk in stomach. It is also used in the production of cheese in industries in the form of cheese.
References
-
Schechter
I., Berger A; On the size of the active site in proteases. I.
Papain;Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communication (1967) 27:
157.
Boros,
Eszter, et al. "Overlapping specificity of duplicated human
pancreatic elastase 3 isoforms and archetypal porcine elastase 1
provides clues to evolution of digestive enzymes." Journal of
Biological Chemistry 292.7 (2017): 2690-2702.
Reis,
Rui L., and Julio San Román, eds. Biodegradable systems in tissue
engineering and regenerative medicine. Crc Press, 2004.
Kohlmeier,
Martin. Nutrient Metabolism: Structures, Functions, and Genes.
Academic Press, 2015.
Rawlings,
Neil D., and Guy Salvesen. "Handbook of proteolytic enzymes,
vol. 3." (2013)
Strauss,
A. W., et al. "Characterization of an endopeptidase involved in
pre-protein processing." Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences 76.9 (1979): 4225-4229
Boyer,
Paul D., ed. Hydrolysis: peptide bonds. Vol. 3. Academic press,
1971.
Zhenyue
Tong, Beate Illek, Vikash J. Bhagwandin, George M. Verghese, and
George H. Caughey. “Prostasin, a membrane-anchored serine
peptidase, regulates sodium currents in JME/CF15 cells, a cystic
fibrosis airway epithelial cell line.” American Journal of
Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2004 287:5,
L928-L935
Berg,
Jeremy M., John L. Tymoczko, and Lubert Stryer. Biochemistry
(Loose-Leaf). Macmillan, 2008.
Keil,
B. Specificity of proteolysis. Springer-Verlag
Berlin-Heidelberg-NewYork, pp.335. (1992)
Rawlings,
Neil D., and Guy Salvesen. "Handbook of proteolytic enzymes,
vol. 3." (2013)
Silveira,
E., et al. "Expanded bed adsorption of bromelain (EC 3.4.
22.33) from Ananas comosus crude extract." Brazilian Journal of
Chemical Engineering 26.1 (2009): 149-157.
Corzo,
Carlos A., Krzysztof N. Waliszewski, and Jorge Welti-Chanes.
"Pineapple fruit bromelain affinity to different protein
substrates." Food Chemistry 133.3 (2012): 631-635.
Silveira,
E., et al. "Expanded bed adsorption of bromelain (EC 3.4.
22.33) from Ananas comosus crude extract." Brazilian Journal of
Chemical Engineering 26.1 (2009): 149-157.
Rowan,
Andrew D., and David J. Buttle. "[38] Pineapple cysteine
endopeptidases." Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 244. Academic
Press, 1994. 555-568.
Risør,
Michael W., et al. "Enzymatic and structural characterization
of the major endopeptidase in the Venus flytrap digestion fluid."
Journal of Biological Chemistry 291.5 (2016): 2271-2287.
Zucker,
Stanley, et al. "The proteolytic activities of chymopapain,
papain, and papaya proteinase III." Biochimica et Biophysica
Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology 828.2 (1985):
196-204.
Elsamadony,
M., et al. "Use of Carica papaya enzymes for enhancement of H2
production and degradation of glucose, protein, and lipids."
Energy Procedia 75 (2015): 975-980.
Henschel,
Michael J., Michael J. Newport, and Veena Parmar. "Gastric
proteases in the human infant." Neonatology 52.5 (1987):
268-272.